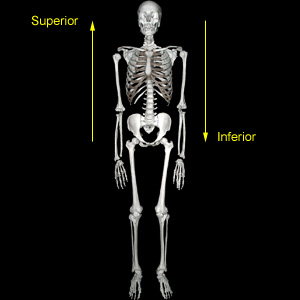
a relative term used for bipedal hominins (those that travel on two legs) to describe features on the trunk that are closer to the feet; the opposite of superior. The term caudal is a synonym commonly used when referring to quadrupedal animals.
a measure of the entire length of the arms in proportion to the entire length of the legs; calculated by diving the length of the humerus and radius, by the length of the femur and tibia, multiplied by 100.
turning the sole of the foot towards the medial portion of the body; opposite of eversion.
eFossils is a collaborative website in which users can explore important fossil localities and browse the fossil digital library. If you have any problems using this site or have any other questions, please feel free to contact us.
Funding for eFossils was provided by the Longhorn Innovation Fund for Technology (LIFT) Award from the Research & Educational Technology Committee (R&E) of the IT governance structure at The University of Texas at Austin.
